Serial Function Block
Serial Interfaces
The SIO07 has one serial interface, labelled RS232/485.
Features
- RS232 or RS485 full-duplex or RS485 half-duplex
- Virtual TTY support using RFC2217
- Appears as a standard TTY device on Linux hosts
- Baud rates up to 460800 baud
- Galvanic isolation between the COM port and other interfaces
- Hardware flow control lines available in RS232 mode
Connection
COM port connector on SIO07:
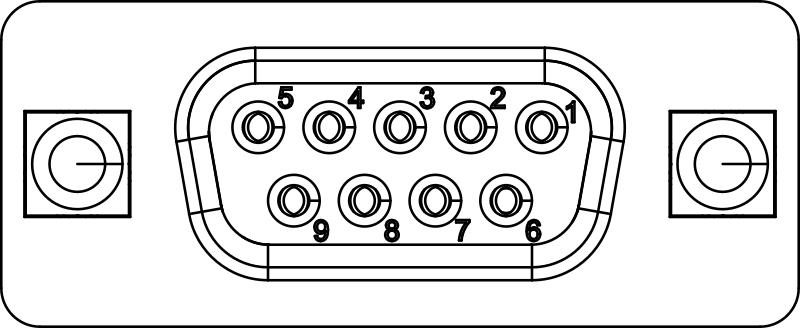
Pin functionality as viewed from SIO07:
| Pin | Symbol | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | RS485_TX+ | RS485 positive transmit line |
| 2 | RS232_TXD | RS232 transmit line |
| 3 | RS232_RXD | RS232 receive line |
| 4 | RS485_RX+ | RS485 positive receive line |
| 5 | GND | Ground (isolated from other interfaces) |
| 6 | RS485_TX- | RS485 negative transmit line |
| 7 | RS232_CTS | RS232 clear to send |
| 8 | RS232_RTS | RS232 request to send |
| 9 | RS485_RX- | RS485 negative receive line |
Typical Connection Examples
Info
Whether you use RS232 or RS485 is defined solely by the hardware wiring. Hardware flow control and half-/full-duplex operation must be configured in software.
Info
For RS485/RS422 half-duplex operation, connect the COM port RX pins with the corresponding TX pins externally.
Info
In RS485/RS422 mode, add termination resistors to the end of the line. The termination must be 120 ohms at each end of the cable.
Serial Function Block
The io4edge TTYnvt function exposes the serial interface of the SIO07 over the network using RFC2217. Clients can connect via TCP and obtain a virtual TTY that behaves like a local serial port.
The module provides a single serial port that is reachable via service name SIO07-1-com and TCP port 10000.
You can use the ttynvt function block utilities from the io4edge SDK or any RFC2217-capable client. Typical workflow:
- Discover the service via mDNS or take the static service name.
- Connect with an RFC2217 client (for example
socatorpyserial). - Configure baud rate, parity, stop bits, hardware handshake according to your peripherals. Hardware handshake is supported.
Example using socat to create a local pseudo terminal:
socat -d -d pty,link=/tmp/com.tty,raw tcp:<module-ip>:10000
Afterwards use /tmp/com.tty like a local serial device from your applications.
